AI algorithms what are the main threats to watch for
Let’s say that you have identified a set of business problems you want to solve and decided to leverage AI-driven solutions to resolve them. After a period of iterating, you find an optimal algorithm that’s well-positioned to solve many of the challenges. Once you put it in production, that’s the end of the story, right?
Well, not really.
There are several risks that could threaten the implementation process. In order to help you understand some of these threats, the European Network and Information Security Agency (ENISA) has prepared a report titled “AI Cybersecurity Challenges” that identifies the eight high-level risk categories shown in the graphic below. Each category has 74 identified threats to AI models.
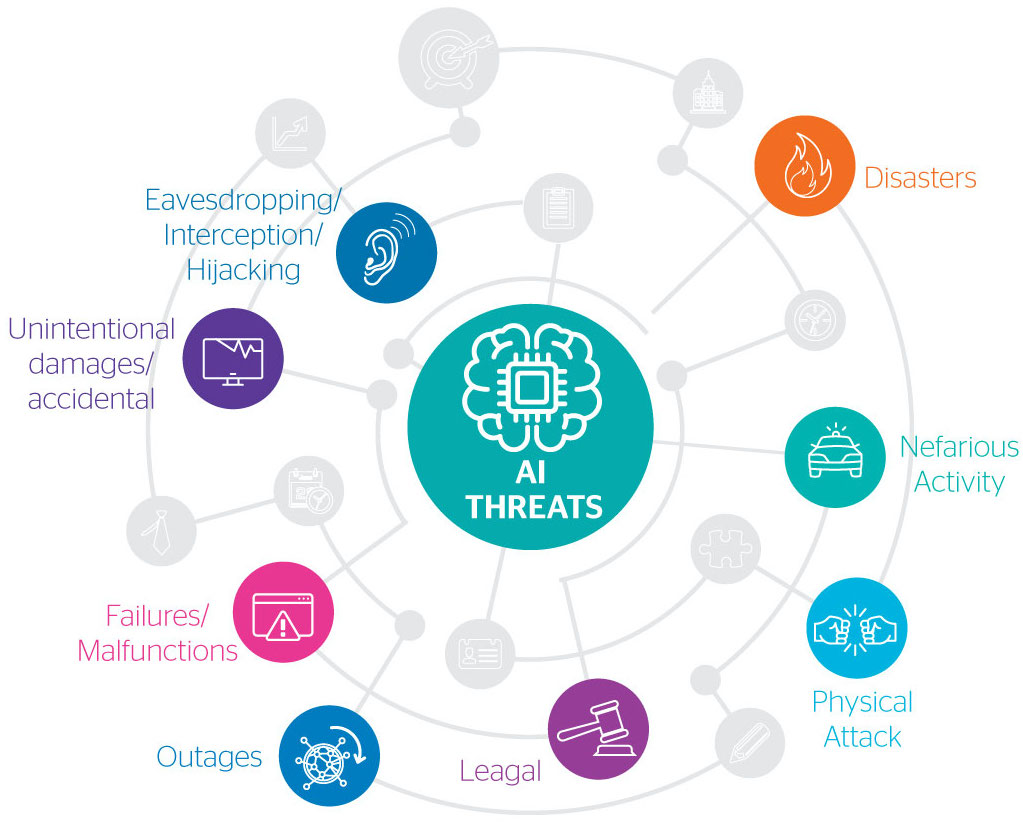
Attacking AI’s security vulnerabilities
Most of these threats are related to data, which is the backbone of any AI system. Data poisoning is one such threat which affects the trustworthiness of a recommender system. For instance, if an attacker manipulates a news portal such that a particular type of news is always recommended to users, then the attacker may be able to change the users’ opinions.
https://arxiv.org/pdf/2101.02644.pdf
Another threat is that of model backdoors. The main goal of this threat is to implant an adversarial vulnerability in the machine learning model during the training phase. For example, imagine that you’re working as an engineer at Tesla and you have trained a model for a self-driving car. One part of the model is specifically trained to detect stop signs. However, someone could inject a backdoor in the model so that when the car sees the stop sign with a small grey circle on it, it will classify it as an invalid sign. That circle is called the backdoor trigger and could cause serious accidents, putting human safety at risk.
How cybercriminals abuse AI
On the other hand, MITRE developed the threat matrix shown below to highlight the seven tactics used in making adversarial attacks on ML systems: reconnaissance, initial access, execution, persistence, evasion, exfiltration and impact. While the ENISA report captures the potential threats that businesses must deal with, MITRE focuses more on the techniques and tactics that potential threat actors use.
Every tactic has many different techniques that can be used. Attackers usually combine techniques from multiple tactics to achieve their goals. For example, a group of ML researchers evaded ProofPoint’s email protection system. They built a copy-cat email protection ML model and used the gathered insights to evade the live system. They did this by combining reconnaissance and evasion tactics.
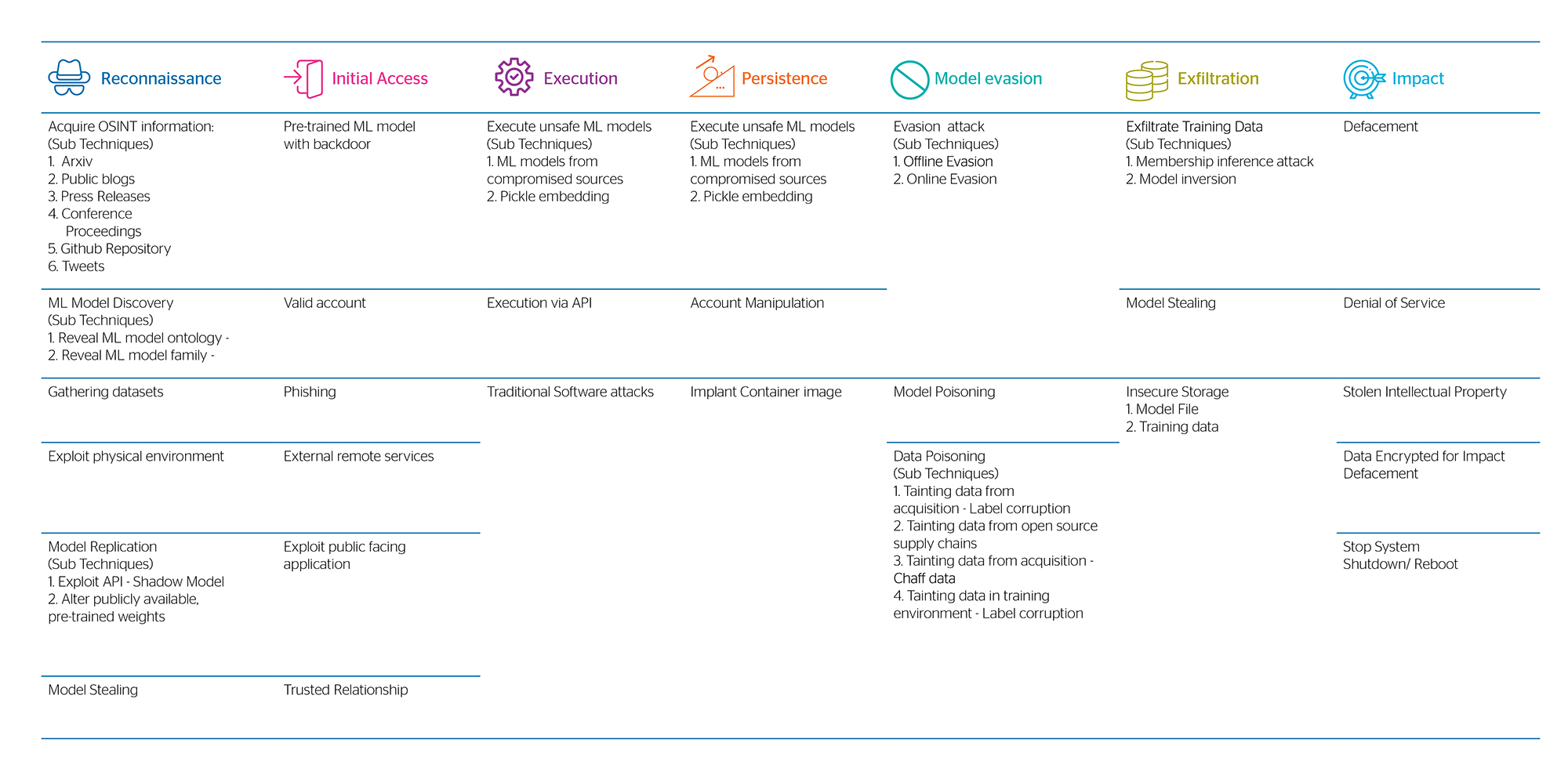
As we’ve demonstrated, it is not sufficient to deploy an AI algorithm in production and let it work unsecured. There’s a huge risk to it that can affect all the business processes. To help you mitigate these risks successfully, Atos provides an AI security assessment to help you understand the threat landscape, and end-to-end cybersecurity solutions with a data-centric and pre-emptive security approach.
About the authors

Tomas Pinjušić
Associate Cybersecurity Consulting Group, Atos
Tomas is an Associate Consultant at Atos. As such, he’s been working closely with senior cybersecurity consultants and assisting them in their initiatives. The main goal of his activities is to help global companies to have a secure ecosystem and go much further in their security aspirations than mere compliance.
He has developed the AI Business & Cybersecurity Maturity Assessment offer which exists to help companies discover how proficient are they with securing their AI models and utilizing cybersecurity solutions with advanced capabilities. In addition, he’s been working on the Partners in the Spotlight webinar initiative and coordinating activites for The Forrester Wave Q3 2021.

Nemanja Krivokapic
Principal Cybersecurity Consulting Group, Atos
Nemanja is a CyS Global Principal Consultant, experienced Cybersecurity Practitioner with 20 years of professional experience, committed, proactive and creative mind in an Ever-changing cybersecurity landscape. His focuses are InfoSec Governance and Strategy, GRC, Management Consulting, and Project transformation programs. He has successfully managed several engagements and he is one of the key contributors to the overall Global practice initiatives. He is PMP, CISM & Data protection certified and he is currently finalizing a master’s in information security.
 Download the magazine overview
Download the magazine overview